
| Links | |
| Books |
 |
|
The following map shows the relationship between elements of the sighting:
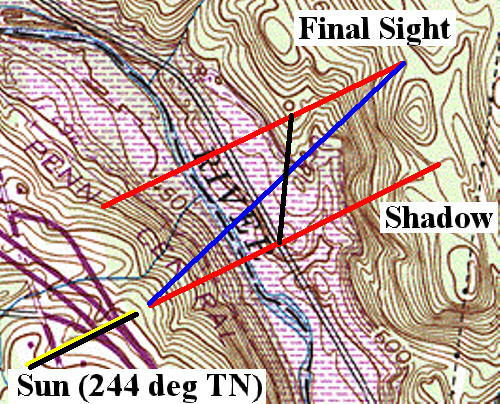
The lower left shows the approximate direction (azimuth) of the sun relative to the sighting at the time of the sighting, according to the sun elevation / azimuth calculator at http://www.cs.ucla.edu/~simonw/sunpos/.
The two red lines represent the location of the object if it were traveling perpendicular to the road at the shadow location or at the final sight location respectively. The blue line is an interpolated course for a high altitude object. The black line connects the shadow crossing with the ridge crossing location.. Theoretically, the actual course could be anywhere between those two, or could even fall outside those courses. However, some sanity tests may be able to be used to constrain the course.
Note that the blue course points almost directly toward the substation. The black course parallels the power line. This may or may not be pertinent.
The most important point to note, however, is that with the sun aligned almost directly perpendicular to the road, there is an opportunity to almost exactly plot the continuum of possible altitudes for the object. The following diagram illustrates this:
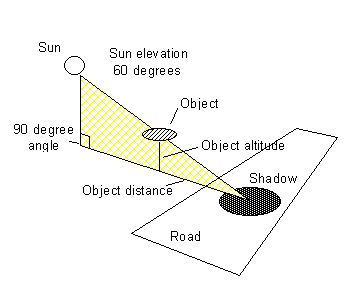
In other words, the object is somewhere along a line between the shadow and the sun. Since the sun is at an elevation of 60 degrees, so is the object. From the resulting right triangle, it is possible to establish an object altitude for any object distance.
Note also that the shadow has a diameter, which is probably close to the size of the object itself.
The course is also constrained, since the witness does not recall anything other than a straight line of movement. In addition, the altitude is constrained, since the witness did not have any sense that the object was engaged in terrain following.
The solution to the placement of the shadow, due to the convenient sun azimuth, resolves to determining the possible position from which the shadow could be cast. That position is somewhere along the shadow line. The distance is based on the right triangle with an elevation angle relative to the shadow spot on the road of 60 degrees. Becuase the distance of the object is unknown, only a range of distances and elevations can be generated.
Between the information provided by the shadow analysis and the fact that the object was not seen by the party witnesses, it is possible to greatly constrain the size, speed, and altitude of the object.
See the observational constraints for the interpretation of these results.
This site is an archive of the content of the MUFON CT website from the late 1990s. The current MUFON CT organization should be contacted through the MUFON web site.